Encryption Algorithms
Symmetric Algorithms
- AES
- RC4
- Serpent
- Blowfish
Asymmetric Algorithms
- RSA
Hashing and Compression
Hashing
- MD5
- SHA
- CRC
Compression
- APLib
- LZNT
- LZMA
Windows API calls to Functions
Encryption/Decryption
CryptAcquireContext()
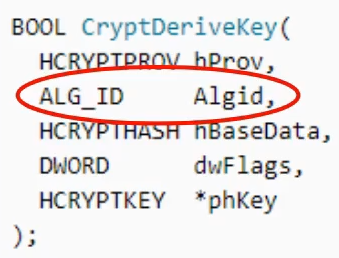
CryptDeriveKey()We can identify the exact crypto algorithm used by looking at the argument passed into this function
CryptEncrypt()
CryptDecrypt()
Compression/Decompression
RtlCompressBuffer()
RtlDecrompressBuffer()
Hashing
CryptAcquireContext()
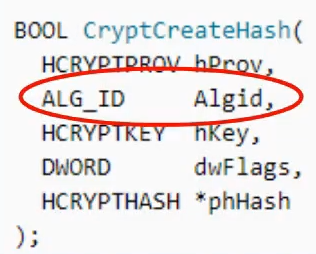
CryptCreateHash()We can identify the exact hashing algorithm used by looking at the argument passed into this function
Recognizing Custom Crypto Implementations
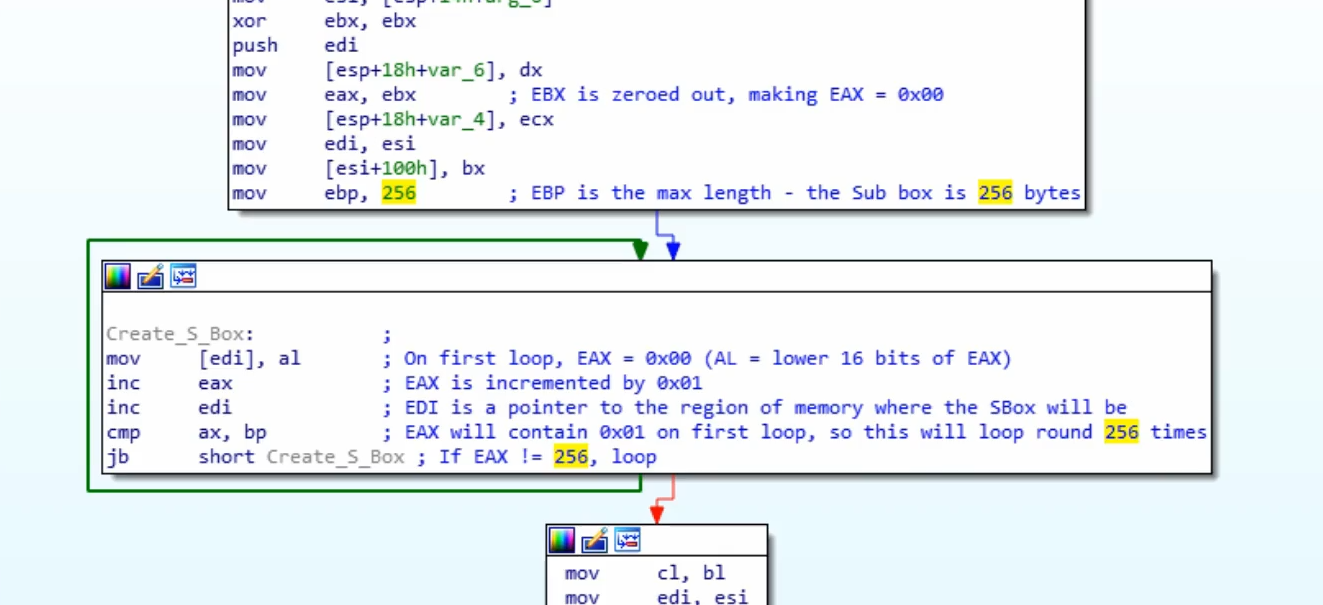
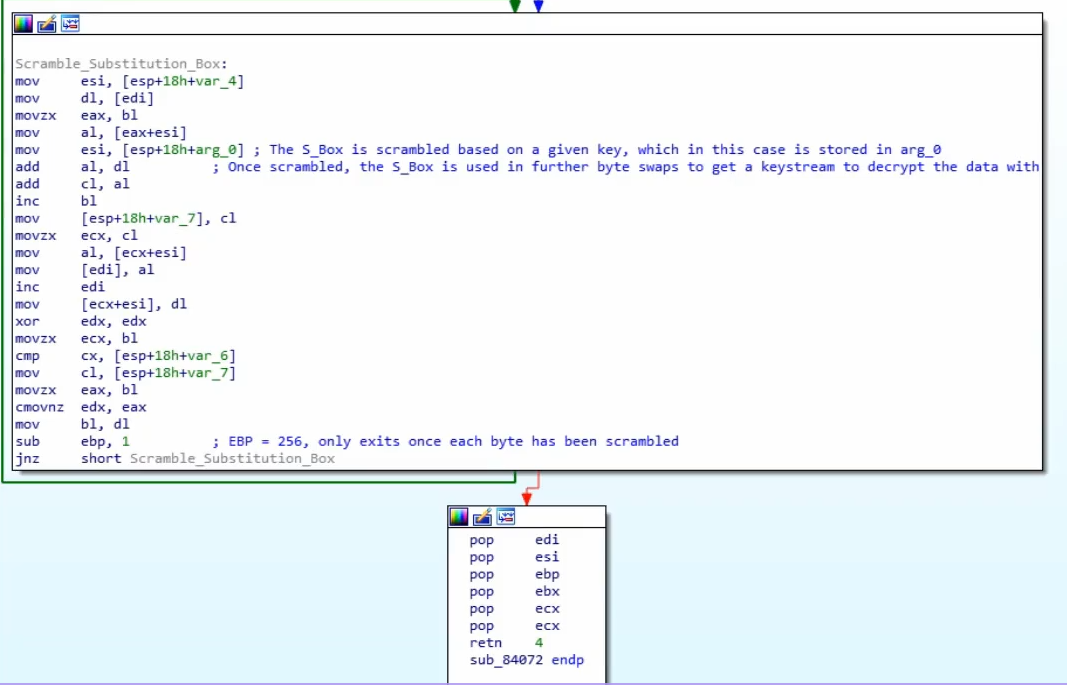
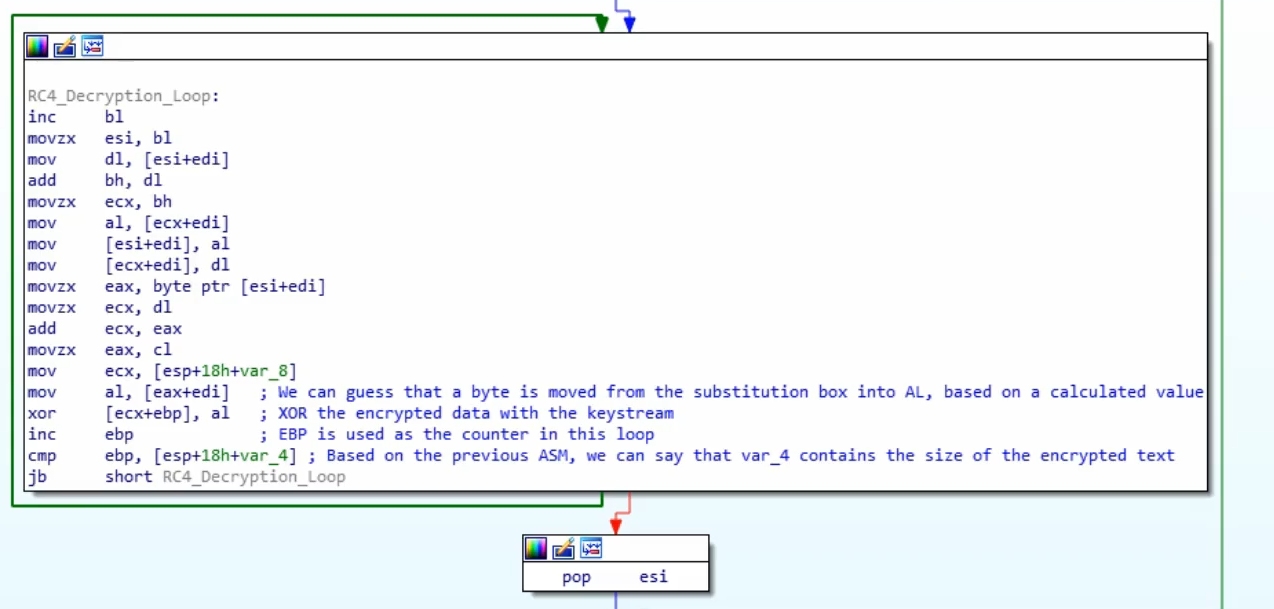
RC4
- Create a Substitution Box in memory
- Scramble the Substitution Box
- Decrypt the data byte-by-byte
- Uses a XOR loop
Other algorithms like AES uses this same approach as well for Encryption/Decryption
Sample code flow for RC4
AES
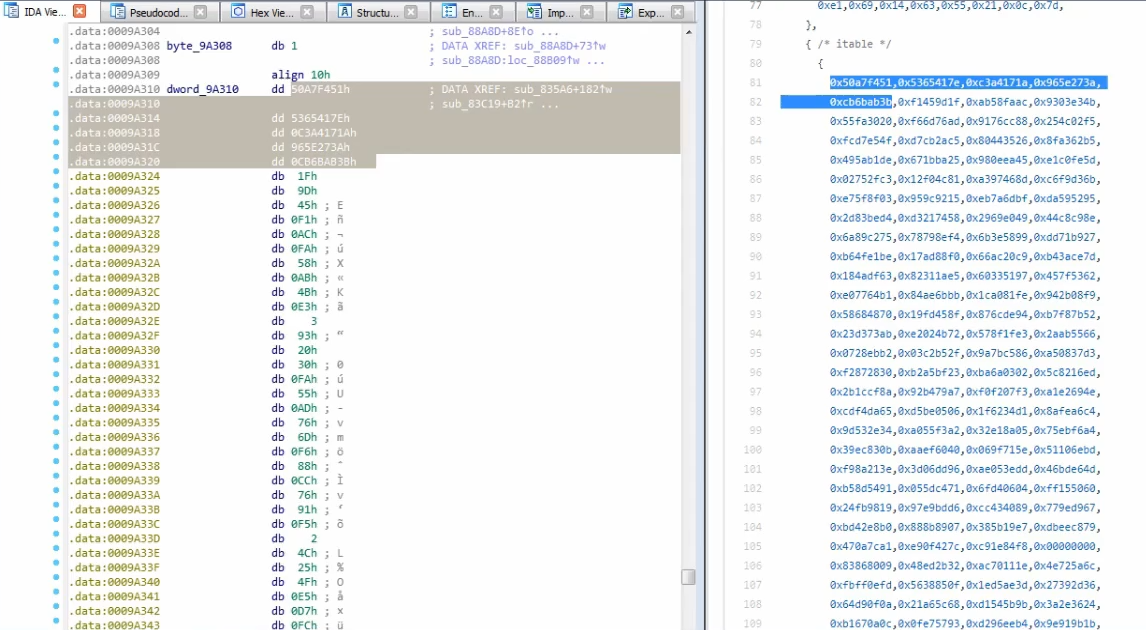
- Similar to RC4 in that AES also uses a Substitution Box, just that AES uses several lookup tables and sub-boxes
- We can identify AES through the use of Crypto Constants, which are constant values present in the lookup tables.
- The decryption key must be divisibly by 16 as the keys are usually 32 bytes. RC4 on the other has keys between 1-256 bytes
Serpent
- Simply identified based in it’s length, as the Serpent algorithm is on large function of encryption
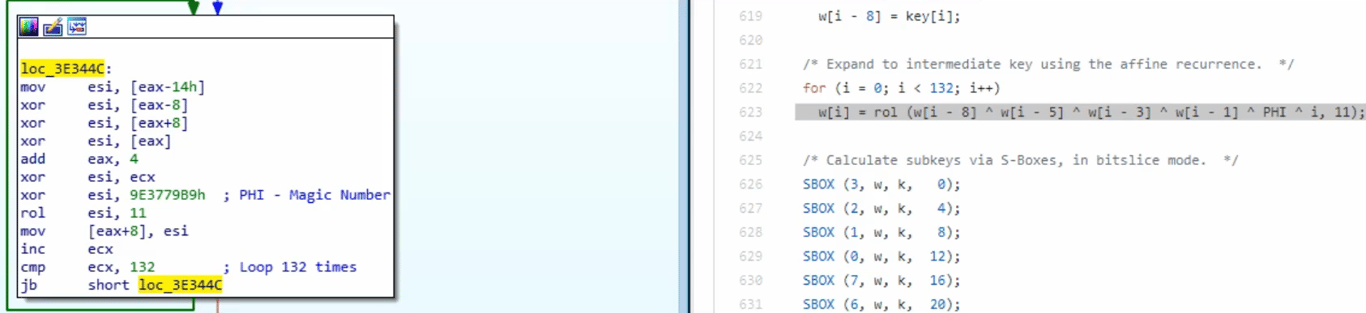
- Constant
9E3779B9appears in the Serpent algorithm as a crypto constant. This also appears in Tiny Encryption Algorithm (TEA)
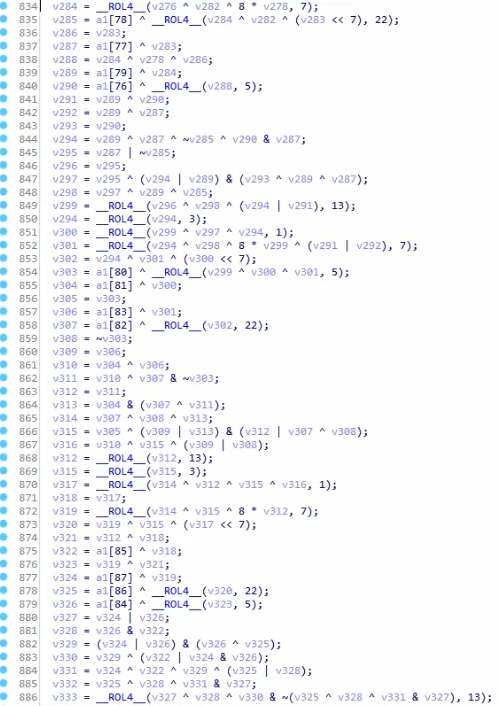
RSA
- More complex than symmetric algorithms
- No crypto constants unlike symmetric algorithms
- An example is Ursnif which uses RSA to decrypt the Serpent key, which is then used to decrypt the rest of the payload
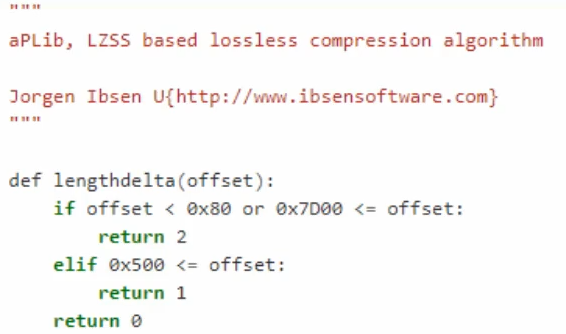
APLib
- No constants used
- Uses 3 compares against constants
- The constants will not always be the same, but you can recognize the 3 compares as clue that it’s using APLib
- Google for any values that show up and add “compression algorithm” the search and pray it shows APLib
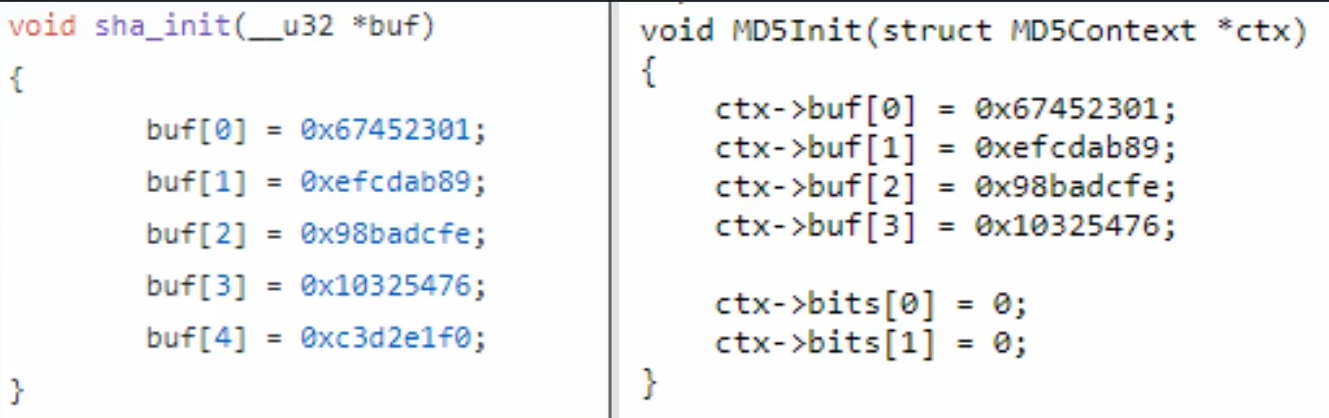
MD5/SHA
init()
update()
final()
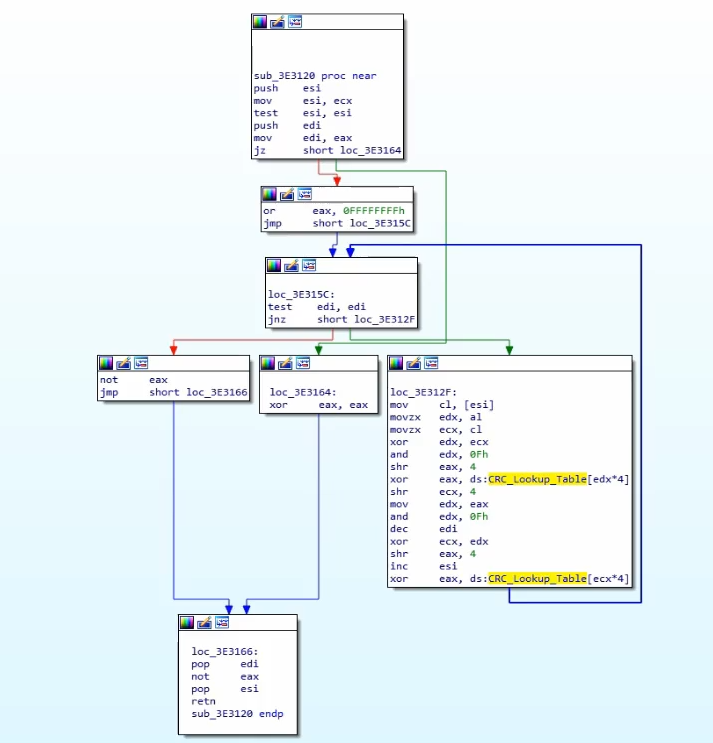
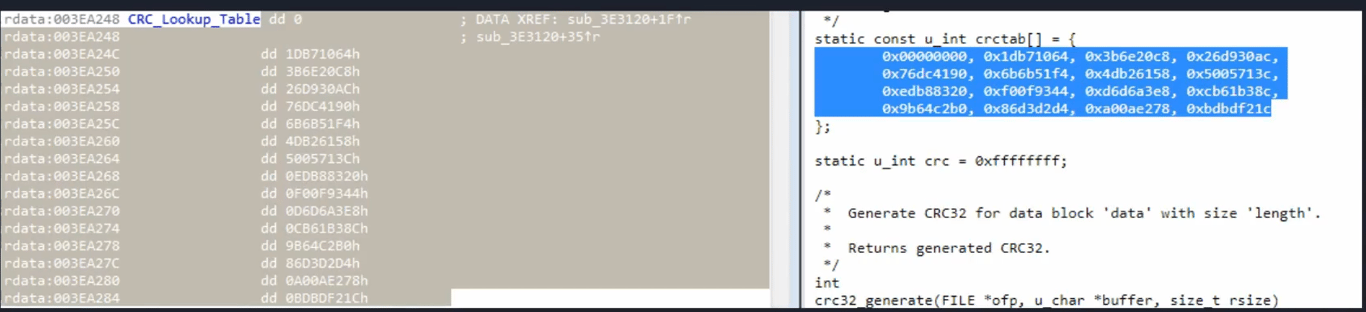
CRC
- Utilizes a lookup table containing constants
- We can search online for these constant to verify if it’s using CRC
Sample code flow for CRC